What Are Essential Oils, and Do They Work?
Essential oils are often used in aromatherapy, a form of alternative medicine that employs plant extracts to support health and well-being.
However, some of the health claims associated with these oils are controversial.
This article explains all you need to know about essential oils and their health effects.
Essential oils are compounds extracted from plants.
The oils capture the plant’s scent and flavor, or “essence.”
Unique aromatic compounds give each essential oil its characteristic essence.
Essential oils are obtained through distillation (via steam and/or water) or mechanical methods, such as cold pressing.
Once the aromatic chemicals have been extracted, they are combined with a carrier oil to create a product that’s ready for use.
The way the oils are made is important, as essential oils obtained through chemical processes are not considered true essential oils.
SUMMARYEssential oils are concentrated plant extracts that retain the natural smell and flavor, or “essence,” of their source.
Essential oils are most commonly used in the practice of aromatherapy, in which they are inhaled through various methods.
Essential oils are not meant to be swallowed.
The chemicals in essential oils can interact with your body in several ways.
When applied to your skin, some plant chemicals are absorbed (
It’s thought that certain application methods can improve absorption, such as applying with heat or to different areas of the body. However, research in this area is lacking (
Inhaling the aromas from essential oils can stimulate areas of your limbic system, which is a part of your brain that plays a role in emotions, behaviors, sense of smell, and long-term memory (
Interestingly, the limbic system is heavily involved in forming memories. This can partly explain why familiar smells can trigger memories or emotions (
The limbic system also plays a role in controlling several unconscious physiological functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. As such, some people claim that essential oils can exert a physical effect on your body.
However, this has yet to be confirmed in studies.
SUMMARYEssential oils can be inhaled or diluted and applied to the skin. They may stimulate your sense of smell or have medicinal effects when absorbed.

Lemonaid has a team of licensed medical professionals who can prescribe name brand or generic ED medication. Get 50% off your first shipment, plus fast, free & discreet delivery right to your door.
There are more than 90 types of essential oils, each with its own unique smell and potential health benefits.
Here’s a list of 10 popular essential oils and the health claims associated with them:
- Peppermint: used to boost energy and aid digestion
- Lavender: used to relieve stress
- Sandalwood: used to calm nerves and help with focus
- Bergamot: used to reduce stress and improve skin conditions like eczema
- Rose: used to improve mood and reduce anxiety
- Chamomile: used to improve mood and relaxation
- Ylang-Ylang: used to treat headaches, nausea, and skin conditions
- Tea Tree: used to fight infections and boost immunity
- Jasmine: used to help with depression, childbirth, and libido
- Lemon: used to aid digestion, mood, headaches, and more
SUMMARYThere are over 90 commonly used essential oils,
Founded in 2008, doTERRA grew rapidly thanks to the vision of a group of passionate people with a mission to share the purest essential oils with the world. They formed a company and named it doTERRA, a Latin derivative meaning “Gift of the Earth.” Watch the story of doTERRA’s genesis. &&&& &&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&7 &&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&7 &&&&&&&&&&&&
5 Secrets to Live Over 100 Years Old (The Science Behind the Longest-Living People on Earth)
Filed in: Health
By Celestine ChuaThis is a guest post by Alexander Heyne of Modern Health Monk.
There are places on earth where, if you don’t make it to 100, it’s almost unusual.
These places have been studied by scientists for decades and have been given a name: blue zones.
As it turns out, blue zones exist only in a few places on earth:
Sardinia, Italy
The islands of Okinawa, Japan
Loma Linda, California
Nicoya, Costa Rica
Ikaria, Greece
But there’s one reason why these people have been studied so much by scientists.
Beyond just living to 100 in much higher rates than virtually anywhere else in the world, these people suffer from a fraction of the health issues that most westerners suffer from in their 30s, 40s, 50s and later.
Dementia, heart issues and depression are almost non-existent among these people. What this means it that these people live a fantastic quality of life their entire (long) lives – not just at the end.
That is why this research is so tremendously valuable to most of us.
What’s Wrong In the West?
In the United States, 50% of the people that die every year die from Heart Disease and Cancer – both of which are somewhat preventable.
We know that there are cultures on earth without heart disease.
And we know that there are cultures on earth without cancer or incredibly low rates of cancer.
And we know that both have a very strong diet and lifestyle component. Yet we haven’t quite figured out why so many people are dying.
What’s amazing is that in these blue zone communities (in particular, Ikaria, Greece) cancer rates are a fraction of what they are in the west, heart disease rates are almost HALF of what they are, and dementia doesn’t even exist.
What that means is that not only do these people rarely get many of the diseases you and I would get (and thus live a more enjoyable, pain-free life), they enjoy optimal health throughout their entire lives – almost until the day they die.
By living a certain lifestyle, not only do you improve your health NOW, this ensures you avoid the major killers later in your life.
So rather than just saying “okay, but what if I don’t want to live to 100?” these suggestions will help you live an optimally healthy and happy life now.
So What Are These Similarities?
Researchers ended up drawing conclusions between three of these particular groups: the Sardinians, the Okinawans, and the Loma Linda, California group.
What’s interesting is that their “secrets” are not all tangible things.
I’m going to introduce you to the five similarities among the groups, which aren’t exactly secrets, and then after I’ll show you the individual secrets each of these cultures had. To me, the secrets are what come after these five.
Here’s what they are:
#1 Family
Family is stressed as the most important thing in the lives of these people. It’s a priority to regularly see them, visit them, and interact with people part of their own tribe. Virtually everything in these cultures revolves around social interaction.
#2 No smoking (obvious)
#3 Plant-based diet
The major part of each meal was plants.
Note: this does NOT mean they didn’t eat meat or carbohydrates. It means that (like I’ve recommended in this six pack article), the foundation of each meal is plants, followed by a smaller portion of meat or refined carbohydrates.
#4 Constant low level of exercise (maybe not what you’re thinking of)
When we usually think of physical activity these days, we usually think of going to the gym and hitting it hard.
In reality, the people that regularly live to be the oldest aren’t going through extreme workouts – they’re just getting regular physical activity like gardening, hiking, or other labor required for farming. And they’re getting this activity every day.
Regular low or moderate level exercise every day is their exercise.
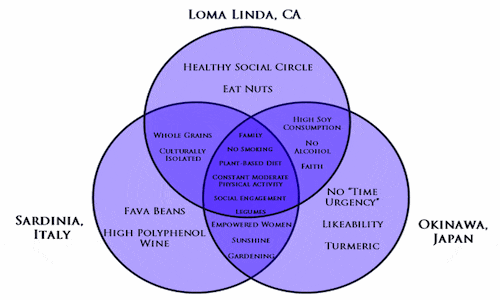
#5 Social engagement
We see “social ties/family” as 2/5 key characteristics of people who live to 100.
Family and social ties make up an entire 30% of this “secret.” Pretty interesting, right?
But what I wanted was specifics. Having a social life is great, but what was it about the specific characteristics of each culture that was enabling them to live to an old age?
The Specific “Secrets” of Each Culture
I want to quickly go into a bit of detail on each culture just so you can see how intangible some aspects of optimal health are. Check out some of the qualities that researchers noted about each culture, that weren’t necessarily as concrete as “diet and exercise.”
The Ikarian Secret
The Ikarians in Greece have 10x the amount of people that reach 100, compared to the United States.
Here are some of the really interesting things, tangible or otherwise, about them:
They put their family first and have really close family ties – stronger social ties have been linked to lower rates of depression and stress (source).
They walk an average of 5 miles a day on uneven terrain (as shepherds).
They drink red wine – where studies usually show back and forth research on alcohol, red wine is packed with antioxidants – what’s interesting is that the Ikarian (like the Sardinian) variety of red wine has three times the normal levels of most red wine.
Ikarians also have a more relaxed outlook on life and laugh whenever possible. (More on the studies behind the Ikarians here.)
The Okinawan Secret
The Okinawans in Japan have a fascinating concept they partly attribute to their long lives, called ikigai – which is a reason for waking up in the morning. It’s almost like a purpose you give to life (or to the day). (Source)
They partly develop this ikigai by having incredibly strong social ties – friends and family that help provide emotional, physical and even financial support (+1 for friends!) (More on ikigai here.)
Many of the local Okinawans have their own gardens that they play in daily (and obviously get food from, too).
The Okinawans also follow a mostly plant diet, but what’s interesting is that they also have a personal rule where they only eat until 80% full, called hari hachi bu.
Some Okinawans in their 90s still even have an active sex life. Talk about impressive!
Nicoya, Costa Rican Secret
The Costa Ricans have a very similar rule as the Okinawans – they have something called a plan de vida – a reason to live (source).
The plan de vida is essentially a purpose or meaning they give to life, which frequently revolves around their social circle or their family. Family is again a huge component of the Nicoya people’s lives.
The Nicoyans also believe in hard work, they rise with the sun, sleep at least 8 hours a night, and eat their biggest meal in the morning – and their smallest meal at night.
***
The Million Dollar Question: Is Longevity “All About” Diet and Exercise?
Honestly, we may never be able to synthesize and write a scientific article on “why” these people live long. We know diet, lifestyle, etc. are critical factors but there are probably many other intangible factors associated with their lifestyle of longevity and great health.
I want to draw your attention to a few interesting things: the intangible aspects of these people’s lives.
Their social circles. The importance of family.
Having a “reason for living.” Working very hard and being active (not in the gym!), but also having a relaxed mental attitude towards life so they aren’t getting overly stressed.
What’s incredibly interesting about these blue zones is that we typically associate longevity and health with fitness and food. In reality, there is an entire mental, social, spiritual and psychological realm that is equally as important.
What About You?
Are you making sure to take into account the intangible aspects of health? Your “social” health, your mental health, your “happiness” health, your spiritual health?
All these factors play much more into health and longevity than you might think. Eating right and exercise are fantastic tools and critical for health, but so is inner cultivation and the cultivation of friendships.
Images: Health, Longevity Diagram
About the Author: Alexander runs Modern Health Monk, a site that shows people how to reverse health problems caused by 21st century life. Check out his free weight-loss crash course, or recent article on fixing neck and shoulder pain for office workers.
For the last several years, various reports have suggested that people are living longer and healthier lives. Better diets and improved medical care have been at the forefront of this trend. If more people are living longer, does this mean more people are reaching the century mark?
In 2005, the US Census Bureau estimated the country would have 114,000 centenarians by the year 2010. The actual number reported in the 2010 census was less than half that amount at exactly 53,364 people. What happened to all the centenarians?
Population of US Centenarians Over Time
Year
|
Number of Centenarians
|
Percentage of Population
|
<1940 div="">
|
rare
|
n/a
|
1950
|
2,300
|
0.0015%
|
1990
|
37,306
|
0.0150%
|
2010
|
53,364
|
0.0173%
|
What People Who Live to 100 Have in Common
U.S. residents in several states live considerably longer than the rest of the country.
By Emily Brandon, Staff Writer Jan. 7, 2013, at 9:30 a.m. More
What People Who Live to 100 Have in Common
A growing number of Americans are living to age 100. Nationwide, the centenarian population has grown 65.8 percent over the past three decades, from 32,194 people who were age 100 or older in 1980 to 53,364 centenarians in 2010, according to new Census Bureau data. In contrast, the total population has increased 36.3 percent over the same time period.
Centenarians in the United States are considerably different from the overall population. Here's a look at some of the characteristics of people who live to age 100:
[In Pictures: States Where People Live the Longest.]
Female gender. It is overwhelmingly women who live to age 100. In 2010, 82.8 percent of centenarians were female. For every 100 females age 100 or older, there are only 20.7 males the same age. Females also make up 61.9 percent of those in their 80s and 72.2 percent of people in their 90s. "We know that women are more social than men. Other studies have found that staying socially connected predicts greater life expectancy," says Gary Small, a professor on aging and director of the UCLA Longevity Center in Los Angeles, who is not affiliated with the Census Bureau report. "If you are social, it may reduce stress levels because you can talk about your feelings and things that stress you out and it seems to help many people. If you need a ride to the doctor or you fall, they can take you to the hospital or help you find the best doctor."
Less diversity. Centenarians are considerably less diverse than the overall U.S. population. In 2010, some 82.5 percent of centenarians were white, versus 72.4 percent of the total population. Black or African Americans were unique in that their proportion of the centenarian population (12.2 percent) is about the same as their percentage of the total population (12.6 percent). Asians made up 2.5 percent of the centenarian population, while they make up 4.8 percent of the total population. And Hispanics represent 5.8 percent of centenarians, but 16.3 percent of the population.
Living with others. Just over a third of both female and male centenarians lived alone in their own home in 2010, but the majority of the oldest citizens live with others. "As people get older, things in life happen—like you might become a widow or you might have a disability, and because of those circumstances, living arrangements often change," says Amy Symens Smith, chief of the age and special populations branch at the Census Bureau. Centenarian females (35.2 percent) were more likely to live in a nursing home than males the same age (18.2 percent). Centenarian males are the most likely to be living with others in a household (43.5 percent), compared to just 28.5 percent of centenarian females.
[Read: How to Finance Life Until 100.]
City living. A large majority of the oldest U.S. citizens live in urban areas. "As age increases, the percentage living in urban areas also increases," says Smith. Some 85.7 percent of centenarians lived in urban areas in 2010, compared with 84.2 percent of those in their 90s, 81.5 percent of those in their 80s, and 76.6 percent of those in their 70s. "Living in the city, you have a lot more mental stimulation and the symphony and better doctors and hospitals and more social networking," says Small. "There are more resources, and there is better transportation."
Located in the Northeast or Midwest. States with the largest populations generally have the most centenarians. California has the largest number of centenarians (5,921), followed by New York (4,605), Florida (4,090), and Texas (2,917). Alaska has the fewest residents age 100 and older (40). Wyoming (72), Vermont (133), and Delaware (146) are also among the states with the fewest centenarians.
The Northeast and Midwest have proportions of centenarians that are higher than the national average of 1.73 per 10,000 people, while the West and South have below-average proportions of centenarians. "There's a lot of stuff going on in local areas, including access to medical care, diet, exercise, the culture, risk-taking, and more smoking," says Linda Waite, a sociology professor and director of the Center on Aging at the University of Chicago. "People in the Northeast tend to be more highly educated, and education is associated with a longer life expectancy." North Dakota is the only state with more than 3 centenarians for every 10,000 people in the state. Other states where centenarians make up a relatively large portion of the population include South Dakota, Iowa, and Nebraska. Three western states have less than one centenarian for every 10,000 people: Alaska, Utah, and Nevada.
[Read: How to Live to 100.]
The proportion of centenarians in the United States is smaller than that of many other developed countries. For example, for every 10,000 people, there are 1.92 centenarians in Sweden, 1.95 in the United Kingdom, and 2.70 in France. And Japan has 3.43 centenarians per 10,000 people, beating even our longest-lived state, North Dakota.
Emily Brandon, Staff Writer
Emily Brandon is the senior editor for retirement at U.S. News & World Report. She has been wri... Read more
Tags: money, aging, retirement, longevity
A low-carb diet for beginners
Studies show that low-carb diets result in weight loss and improved health markers, and these diets have been in common use for decades.
************************LO CARB****MEALS ****WEIGHT LOSS***** ***************************
1. Introduction to low carb
A low-carb diet means that you eat fewer carbohydrates and a higher proportion of fat. This can also be called a low-carb, high-fat diet (LCHF) or a keto diet.**********************GREAT MEALS READY TO GO******************** *******************GREAT GLUTEN FREE BREADS**************** ***************************GRAB AND GO SNACKS************************** **********************************GREAT GRANOLA*******FIND BRANDS AND ITEMS YOU WON'T FIND ANYWHERE ELSE*******************
The basics
- Eat: Meat, fish, eggs, vegetables growing above ground and natural fats (like butter).
- Avoid: Sugar and starchy foods (like bread, pasta, rice, beans and potatoes).
Who should NOT do a strict low-carb diet?
Most people can safely start a low-carb diet.- Are you taking medication for diabetes, e.g. insulin? Learn more
- Are you taking medication for high blood pressure? Learn more
- Are you currently breastfeeding? Learn more
This guide is written for adults with health issues, including obesity, that could benefit from a low-carb diet.
Controversial topics related to a low-carb diet, and our take on them, include saturated fats, cholesterol, whole grains, red meat and restricting calories for weight loss.
Getting started fast
Do you want to get going with low carb right away? Make it truly simple by signing up for our free two-week low-carb challenge. Or get unlimited meal plans, shopping lists and much else with a free membership trial.In 60 seconds
Does low carb still seem complicated? Check out our visual low-carb in 60 seconds guide2. What to eat on a low-carb diet
In this section you can learn exactly what to eat on low carb, whether you prefer visual guides, detailed food lists, delicious recipes or a simple get started guide.Let’s start with a quick visual guide to low carb. Here are the basic food groups you can eat all you like of, until you’re satisfied:

The numbers above are grams of digestible carbs per 100 grams (3.5 ounces). Fiber is not counted, you can eat all the fiber you want.
Detailed low-carb foods list
Try to avoid
Here’s what you should not eat on low carb – foods full of sugar and starch. These foods are much higher in carbs.
The numbers are grams of digestible carbs per 100 grams (3.5 ounces), unless otherwise noted.
Detailed list of foods to avoid
What to drink

What drinks are good on a low-carb diet? Water is perfect, and so is coffee or tea. Preferably use no sweeteners.
For more, check out our complete guides to low-carb drinks and low-carb alcohol.





ReplyDeleteCureidea tracy anderson diet keto liquid diet guaranteed weight loss pills 3 very best (and Worst) Fat Loss SupplementsALL the foremost SUPPLEMENT corporations CLAIM to possess the simplest SUPPLEMENTS FOR FAT LOS AND MOST area unit LYING. HERE’S the reality.Frankly, I don’t like this subject. Among all genres of supplements fat burners area unit enclosed by the foremost info and blatant lies.guaranteed weight loss pills We’re looking associate degree fatness epidemic and it’s reaching way more than simply the USA. I mean, a 3rd of the complete damn world is overweight in step with BMI. The. Entire. World.Can’t blame the U.S. for being fat this point, though you’re positively up there (no worries, we’re still pretty fatover here in our Canadian igloosIt’s clearly a problem of habit formation, easy accessibility to food that happens to be unhealthy however Ohiothus delicious, and a society that places a lot of price on mind than body resulting in plenty a lot of inactive work than before. keto cleanse
http://www.cureidea.com/